近日,我实验室杨斌副教授团队在《Journal of Hydrology》线上发表了题为《Biogeochemistry of dissolved and particulate phosphorus speciation in the Maowei Sea, northern Beibu Gulf》的科研成果。《Journal of Hydrology》当前影响因子为4.5,JCR分区为Q1,是水文学领域历史最悠久、最有影响力的国际期刊之一,也是地学领域的Top期刊。

本研究以茅尾海主要入海河口区为研究区域,于2018年7月现场采集15个站位表层水样品(Fig. 1),分析水体溶解相和颗粒相中各形态磷的浓度,结合水文、化学、生物等参数,对不同形态磷的分布特征、影响因素、迁移转化及生物有效性进行系统研究。
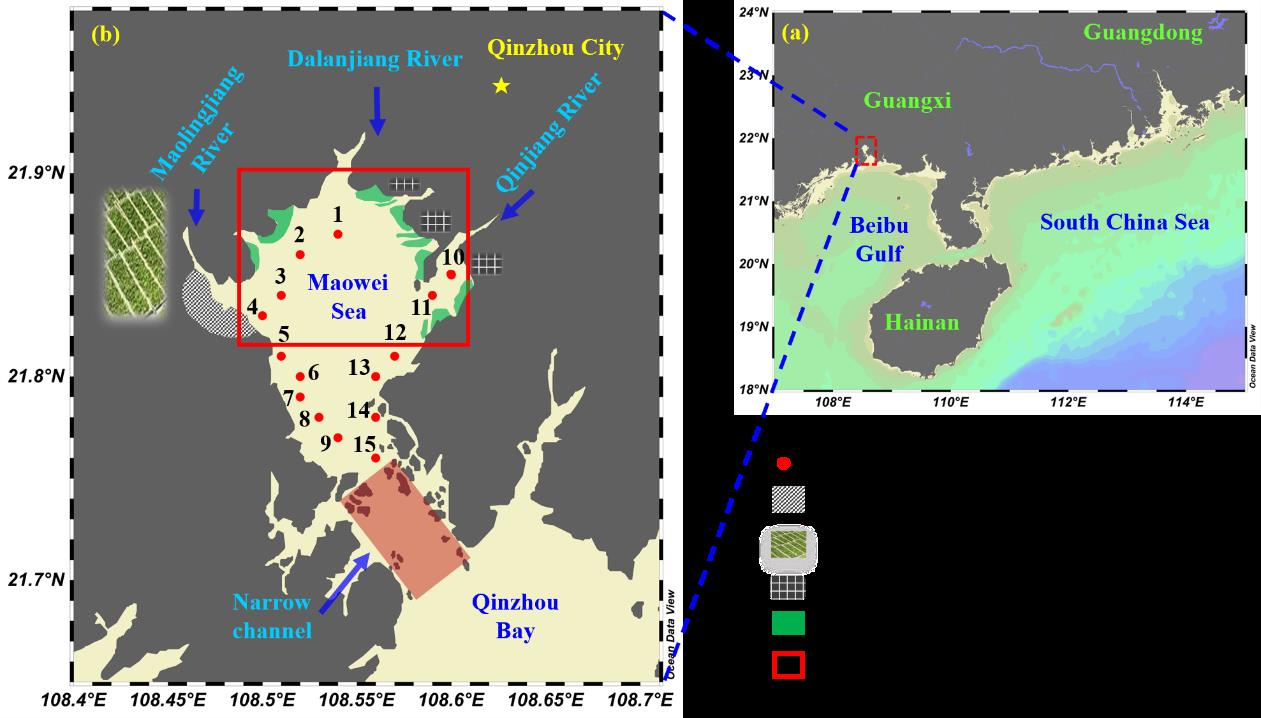
Fig. 1. Map of (a) the study location and (b) sampling sites in the Maowei Sea, northern Beibu Gulf
研究发现,总溶解态磷(TDP)是茅尾海主要入海河口区水体中总磷的主要存在形式,总颗粒态磷(TPP)所占比例相对较小。溶解有机磷(DOP)是水体溶解相中TDP的主要赋存形态,颗粒无机磷(PIP)是水体颗粒相中TPP的主要赋存形态(Fig. 2)。水体不同形态磷的浓度分布受河流输入、水文环境、生物过程和水动力条件等综合因素的影响。水体中磷存在较强的颗粒活性,其在溶解相和颗粒相磷分配过程中具有重要作用,同时受物理、化学和生物因素的共同控制。二端元混合模型计算表明,浮游植物吸收移除水体DIP浓度范围为1.24–1.55 μM(Fig. 3)。
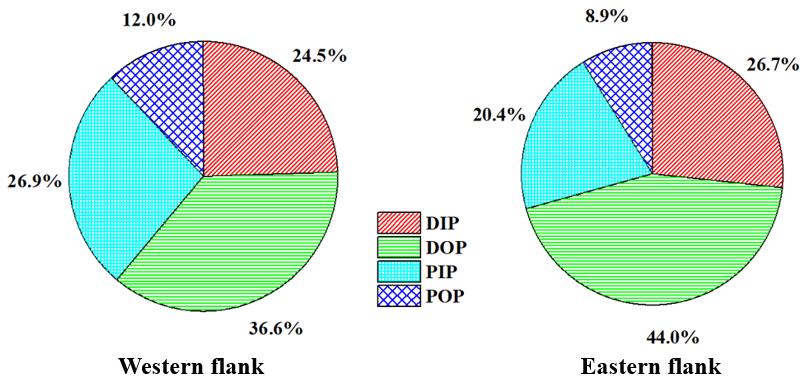
Fig. 2. Surface water proportions of dissolved inorganic P (DIP), dissolved organic P (DOP), particulate inorganic (PIP) and organic P (POP) in total P (TP) pool at the western and eastern flanks of the Maowei Sea.

Fig. 3. The surface water phosphorus partitioning coefficients [log(Kd)] against salinity gradients (a) and log[SPM] (b), as well as theoretical mixing (c) and deviations of DIP (d) against salinity based on two-end-member mixing model at the western and eastern flanks of the Maowei Sea.
该论文第一署名单位是广西北部湾海洋灾害研究重点实验室(北部湾大学),文章共同第一作者为徐程硕士研究生(导师:杨斌副教授)、Solomon Felix Dan博士,通讯作者为杨斌副教授。该研究由国家自然科学基金(41706083, 41466002)、广西自然科学基金(2018GXNSFDA281025, 2018GXNSFAA281295)、广西“海洋生态环境”院士工作站能力建设(桂科AD17129046)共同资助完成。
文章详细信息:
Cheng Xu, Solomon Felix Dan, Bin Yang*, Dongliang Lu, Zhenjun Kang, Haifang Huang, Jiaodi Zhou, Zhiming Ning. Biogeochemistry of dissolved and particulate phosphorus speciation in the Maowei Sea, northern Beibu Gulf. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 593, 125822.
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125822